co2-3 molecular geometry|5.2: Molecular Shape : Baguio One needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure helps in knowing the arrangement of electrons in the molecules and the shape of the molecule. To know the lewis . Tingnan ang higit pa For Final Fantasy: Brave Exvius on the Android, a GameFAQs message board topic titled "List of all Experience booster equipment and materias".
PH0 · Molecular Geometry (Shape) for CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
PH1 · CO3 2
PH2 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Molar
PH3 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry and Hybridization
PH4 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and MO Diagr
PH5 · CO2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Molecular Geometry, and
PH6 · CO2 (Carbon dioxide) Lewis structure
PH7 · 9.2: VSEPR
PH8 · 5.2: Molecular Shape
PH9 · 3D Model of C02
PH10 · 10.3: VSEPR Geometry
Cupang is a barangay in the Muntinlupa, Metro Manila, Philippines. [2] The total land area of the barangay is 5.370 km 2 (2.073 sq mi). It has a population of 57,196 as of the 2020 census. It is located in the northern section of the city.
co2-3 molecular geometry*******The molecular Geometry of any compound is based on the arrangement of atoms, electron pairs, and bonds. Here in CO2, both Oxygen atoms form sigma bonds with the central carbon atom and complete their octet. As a result, there are no lone pairs of . Tingnan ang higit paThe electronic configuration of the Carbon atom in its ground state is 1s22s22p2, and that of an Oxygen atom is 1s22s2p4. When the . Tingnan ang higit paOne needs to know the Lewis structure in order to understand the molecular geometry of any given molecule. This structure helps in knowing the arrangement of electrons in the molecules and the shape of the molecule. To know the lewis . Tingnan ang higit pa A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO3 2- including a description of the CO3 2- bond angles.Looking at the CO3 2- Lewis structure we can see th.co2-3 molecular geometryAssign an AX m E n designation; then identify the LP–LP, LP–BP, or BP–BP interactions and predict deviations from ideal bond angles. Describe the molecular geometry. We will illustrate the use of this .
Use Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) to determine the molecular geometry around each carbon atom and then deduce the structure of the molecule as a whole. Solution: Because the carbon atom on the left is bonded to . Contents show. CO2 Lewis Structure. The lewis structure of CO2 can be with some simple steps, but before that, it is important to understand lewis structure properly. . Wayne Breslyn. 783K subscribers. Subscribed. 65. 2.5K views 5 months ago. How to find the molecular geometry for the CO2 molecule (Carbon dioxide). Molecular Visualization App:.Two regions of electron density around a central atom in a molecule form a linear geometry; three regions form a trigonal planar geometry; four regions form a tetrahedral geometry; five regions form a trigonal .
The Lewis structure for CO2 helps us understand the bonding between the carbon and oxygen atoms and predict the molecule’s geometry, polarity, and reactivity. It also .
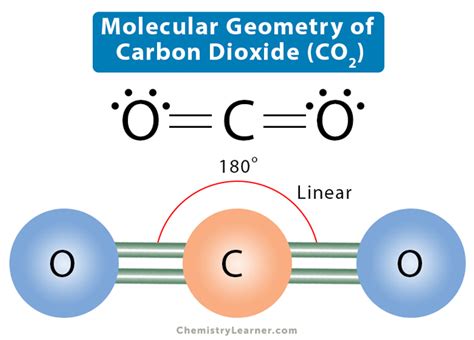
Contents. CO2 Lewis Structure. CO2 Molecular Geometry and Shape. CO2 Bond Angle. CO2 Hybridization. CO2 Molar Mass. CO2 Acid or Base. CO2 Polar or Nonpolar. CO2 Lewis Structure. CO2 has . This is a three-dimensional rendering of carbon dioxide. Click on the structure to rotate it and view it from various angles.From Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) we see that with three bonding pairs around the central atom, the molecular geometry of BCl 3 is trigonal planar, . Two of the oxygens have three lone pairs. One ocht oxygens has 2 lone pairs and is double bonded to the carbon. The molecule has a minus 2 charge. 3. All electron groups are bonding pairs (BP).5.2: Molecular Shape Figure 4.3.9 4.3. 9. Thus, the electron-pair geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular structure is bent with an angle slightly less than 109.5°. In fact, the bond angle is 104.5°. Figure 4.3.9 4.3. 9: (a) H 2 O has four regions of electron density around the central atom, so it has a tetrahedral electron-pair geometry.Here are some examples: H 2O we need to consider the central atom of water which is oxygen. The oxygen has two bonding electron pairs (single bond to each H) and two non-bonding pairs giving water a AX2E2 . CH3OH Molecular Geometry. Now that we know the Lewis structure of CH3OH, it is easy to depict the compound’s molecular geometry. While drawing the Lewis structure for CH3OH, you will notice that the Carbon atom will have three bonds with three hydrogen atoms and one bond with the Hydroxyl Group. Well, this one’s pretty simple. The CHCl3 molecule comprises three chlorine atoms and a Hydrogen atom; all pulled together by the central carbon atom. There are four covalent bonds present- 3 C-Cl bonds and 1 C-H bond. This structure gives rise to four electron domains. As such, the hybridization of the central Carbon atom is sp3. CHCl3 . As CO2 is a neutral molecule, C and A will be 0 here. Finally, H = ½ [4] = 2 = Sp hybridization. These two ways are commonly used to understand the hybridization of CO2. CO2 Molecular Geometry. CO2 has a linear shape. The bond angle of CO2 is 180°. The molecular geometry of any compound can be determined by the VSEPR theory.Figure 5.2.2 5.2. 2: The BeF2 molecule adopts a linear structure in which the two bonds are as far apart as possible, on opposite sides of the Be atom. Figure 5.2.3 5.2. 3 illustrates this and other electron-pair geometries that minimize the repulsions among regions of high electron density (bonds and/or lone pairs).
Count the number of electron groups around each carbon, recognizing that in the VSEPR model, a multiple bond counts as a single group. Use Figure 5.1.3 to determine the molecular geometry around each carbon atom and then deduce the structure of the molecule as a whole. Solution: Carbonate ion (CO32-) Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry or shape, electron geometry, bond angle, formal charge, hybridization. CO 32- is the chemical formula for carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion composed of 1 carbon and 3 oxygen atoms. It is present in a carbonate salt i.e., a salt of carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ).

From Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\) we see that with three bonding pairs around the central atom, the molecular geometry of BCl 3 is trigonal planar, . Two of the oxygens have three lone pairs. One ocht oxygens has 2 lone pairs and is double bonded to the carbon. The molecule has a minus 2 charge. 3. All electron groups are bonding pairs (BP). COCl2 is a chemical compound, known by the name ‘phosgene’. Phosgene is a colorless gaseous compound known as carbonyl chloride and has a molecular weight of 98.92 gram/mol. It is .
co2-3 molecular geometry 5.2: Molecular Shape COCl2 is a chemical compound, known by the name ‘phosgene’. Phosgene is a colorless gaseous compound known as carbonyl chloride and has a molecular weight of 98.92 gram/mol. It is . the central oxygen atom in the ozone molecule, O 3 (g) each of the carbon atoms in propyne, CH 3 CCH (h) the carbon atom in Freon, CCl 2 F 2 (i) each of the carbon atoms in allene, H 2 CCCH 2; . Name the electron group geometry and molecular structure and predict the bond angle. Then click the check boxes at the .
Carbon forms one single bond with the Hydrogen atom and forms a triple bond with the Nitrogen atom. HCN has a total of 10 valence electrons. It is covered under AX2 molecular geometry and . The geometry of BCl3 BCl 3 is also given in Figure 7.2: it is trigonal planar, with all four atoms lying in the same plane, and all Cl−B−Cl Cl − B − Cl bond angles equal to 120o 120 o. The three Cl Cl atoms form an equilateral triangle. The Boron atom has only three pairs of valence shell electrons in BCl3 BCl 3. The rest 28 electrons are non-bonding electrons. Carbon completes its octet by forming bonds with four chlorine atoms. The hybridization of CCl4 is sp3 and has a tetrahedral shape. The bond angle is 109.8 degrees between the lone pairs of electrons and it is nonpolar. Carbon Tetrachloride was first synthesized as a by-product in the .
Count the number of electron groups around each carbon, recognizing that in the VSEPR model, a multiple bond counts as a single group. Use Figure 5.1.3 to determine the molecular geometry around each carbon atom and then deduce the structure of the molecule as a whole. Solution: A quick explanation of the molecular geometry of CO2 including a description of the CO2 bond angles.We can see that there are only two atoms attached to the . 7.1.1 The Ground State of Carbon Dioxide and Its Geometry. In its electronic ground state, the carbon dioxide molecule has a linear geometry (Fig. 7.1) and belongs to the point group D ∞h. Both C-O bonds are equivalent with an equilibrium distance equal to 116.00 pm, as established by electron diffraction [ 1 ].
Today, the City of Cincinnati filed a lawsuit against VineBrook Homes and its Cincinnati affiliates. The complaint alleges that VineBrook breached its settlement agreement regarding a 2021 lawsuit, in addition to claims of public nuisance, civil conspiracy, and intentional, repeated violations of both the Ohio Landlord Tenant Act .
co2-3 molecular geometry|5.2: Molecular Shape